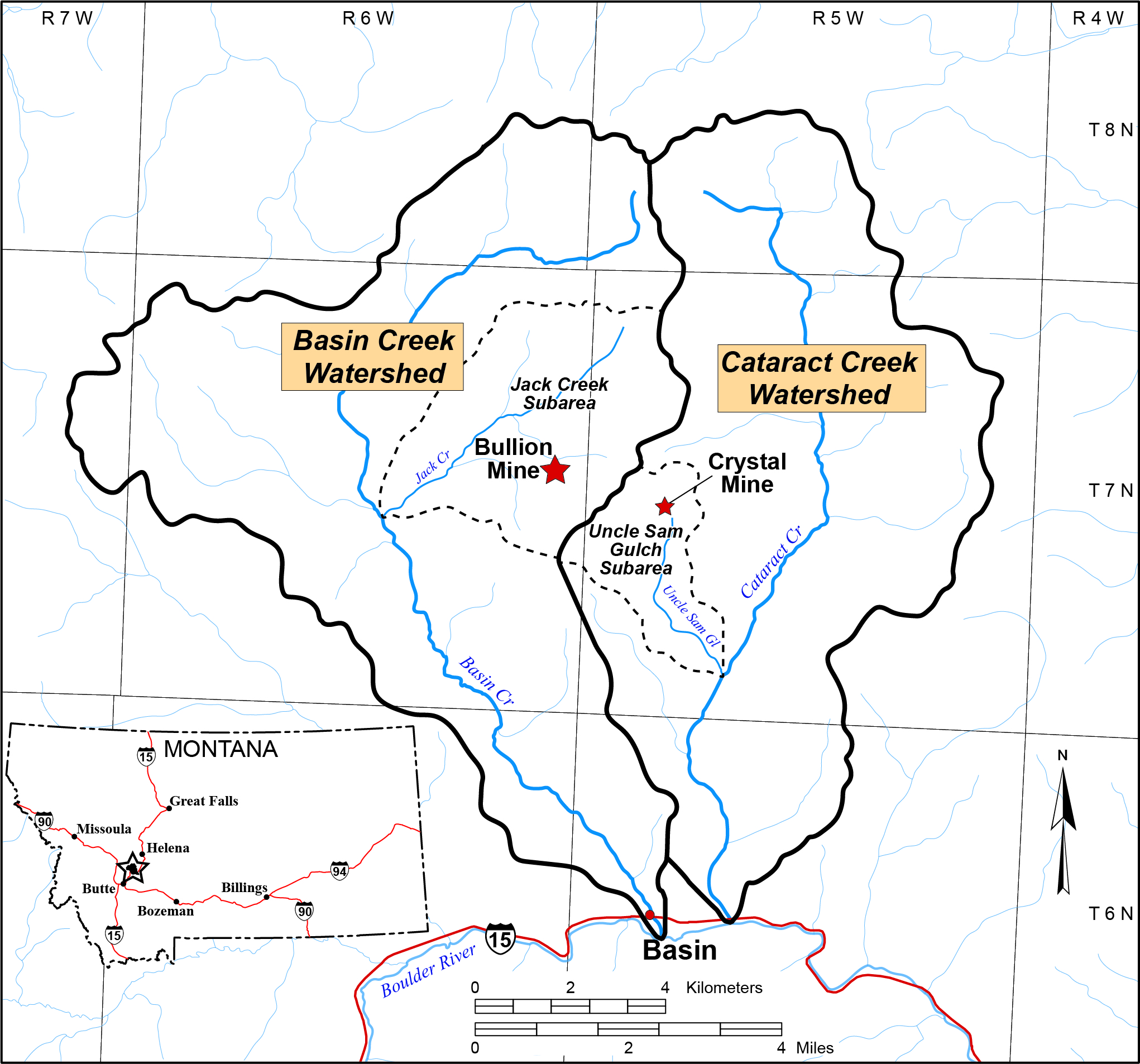
Basin Watershed
- Basin mining district Superfund site
- 300 abandoned hard rock mine sites in 77-square-mile watershed
- The Bullion and Crystal Mines are the two major threats to surface-water quality
This map shows locations of active projects; please scroll down for more information about each project.
Program Information
Office locations in Butte and Billings
Ted Duaime Hydrogeologist—Assistant Professor
(406) 496-4157 | Email
Gary Icopini Hydrogeologist—Professor
(406) 496-4841 | Email
Steve McGrath Geochemist—Assistant Professor
(406) 496-4157 | Email
Jackson Quarles Hydrogeologist—Professional Scientist
Email
John Roitz Water Resource Specialist
Email
Matthew Vitale Hydrogeologist—Professional Scientist
Email
Office locations in Butte and Billings
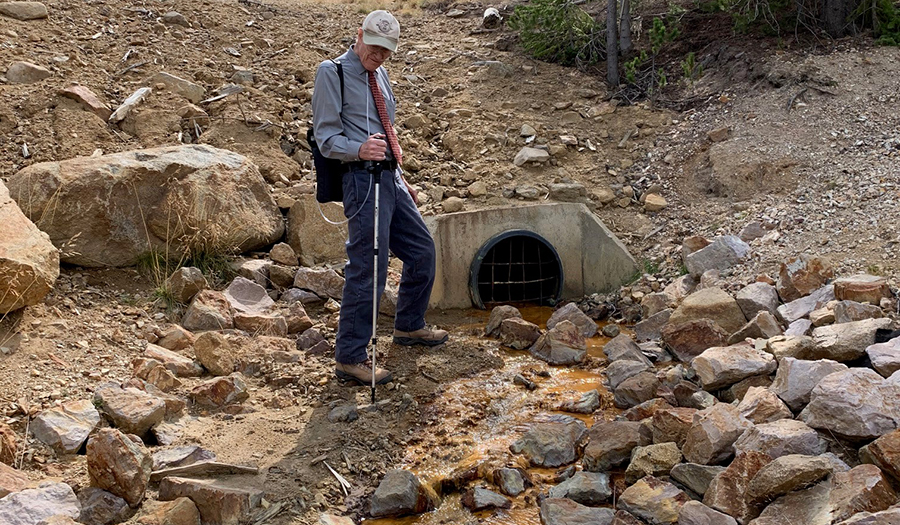
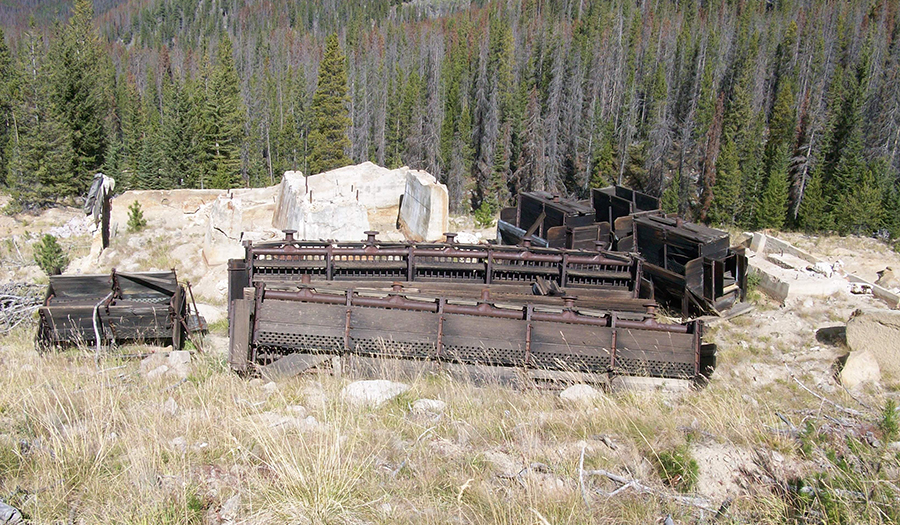
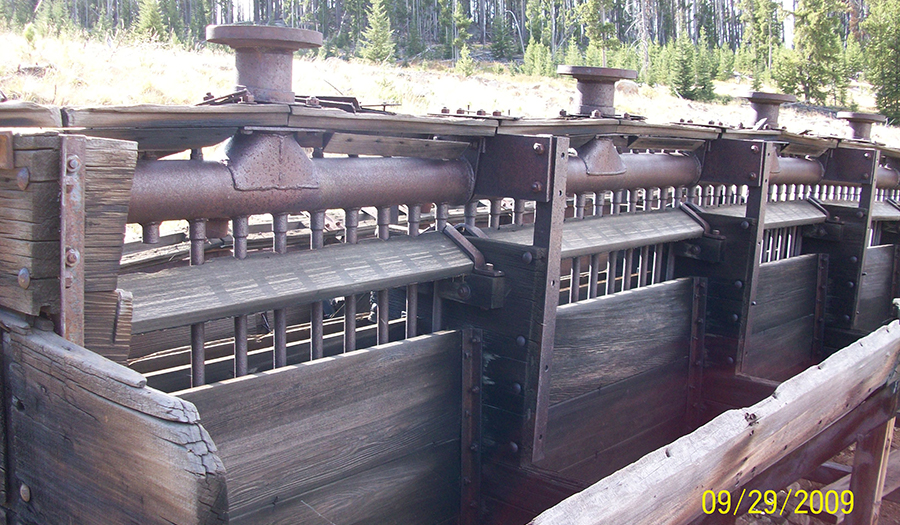
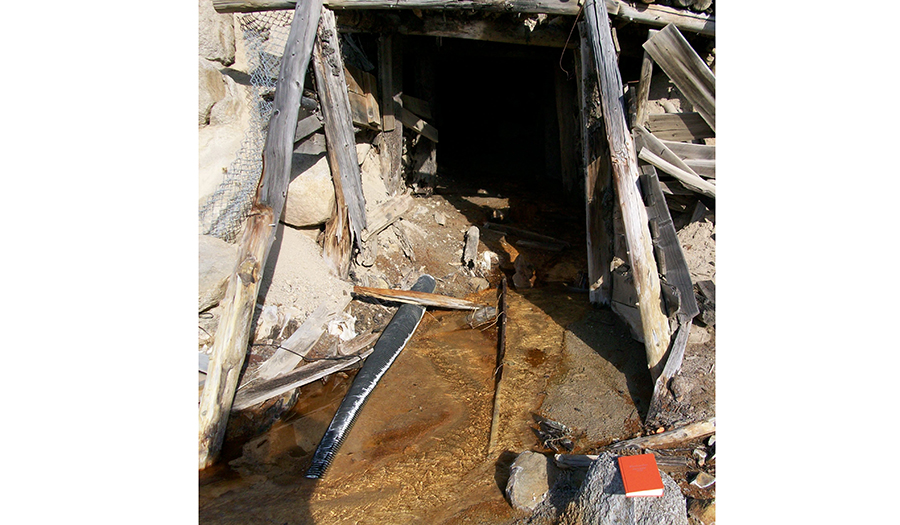
Bullion Mine Site
- 1897–1974 mining of gold, silver, copper, lead, and zinc
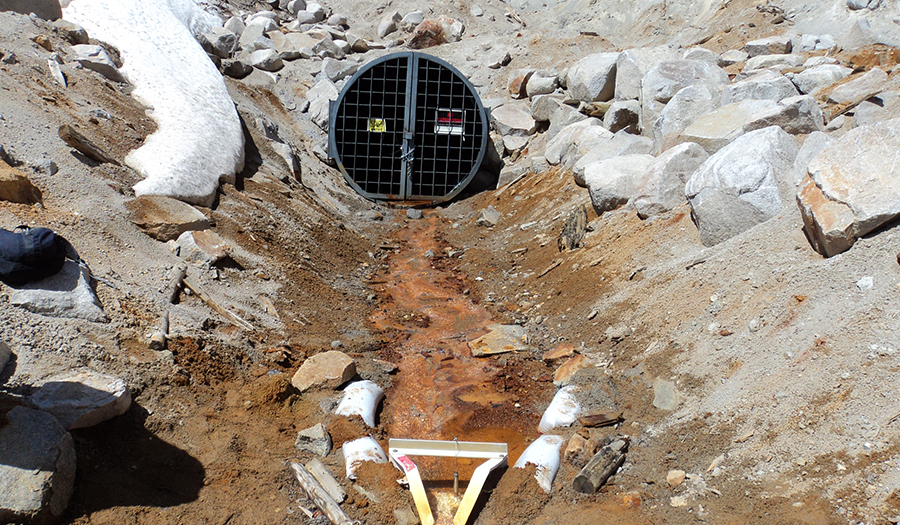
- Mined on three levels; the main adit extended about 4,500 ft to the east along the mineralized structure
- Surface water and groundwater infiltrate through the fractured bedrock into the mine workings
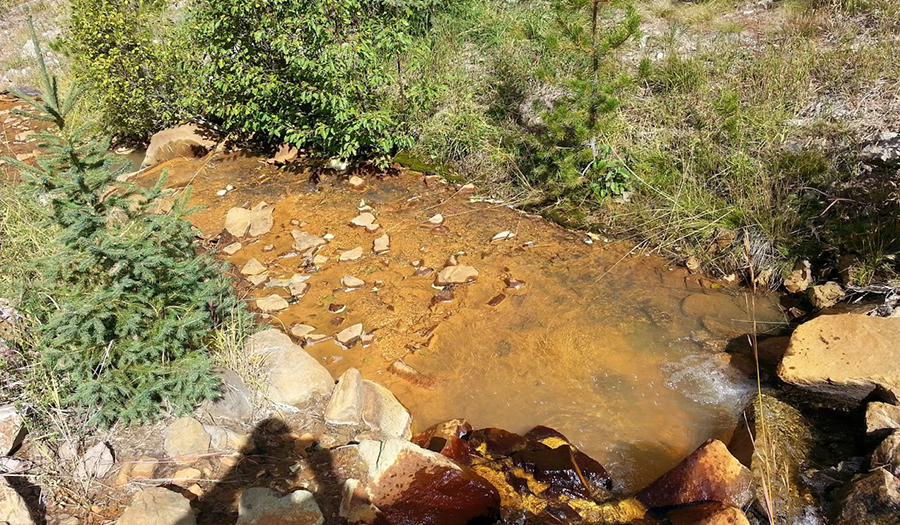
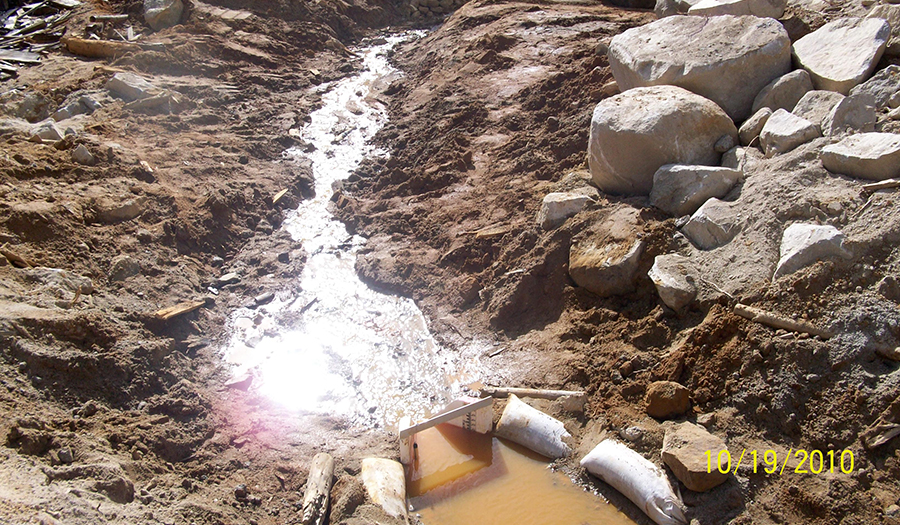
- Acid mine drainage (lower adit) is the main source of impact on Jack Creek, which is a tributary to Basin Creek
- Elevated arsenic and metals are found in sediment at the discharge to Jack Creek
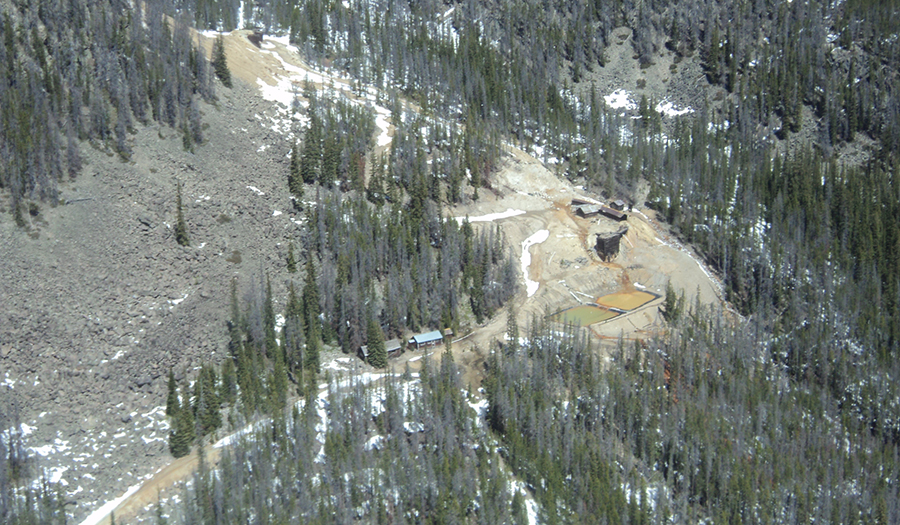
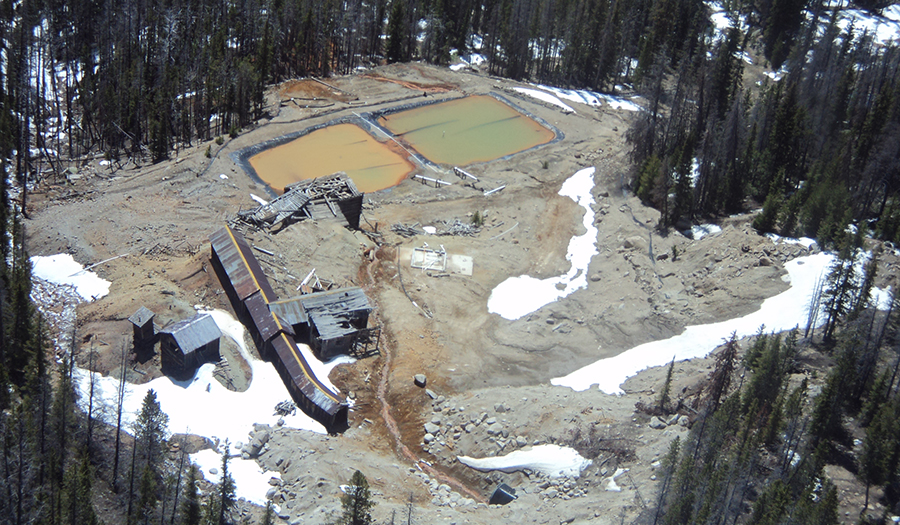
Crystal Mine Site
- Located at the head of Uncle Sam Gulch within the Cataract Creek drainage
- 1883–1984 Mining of copper, lead, and zinc ore, which was generally shipped to Basin or East Helena for processing
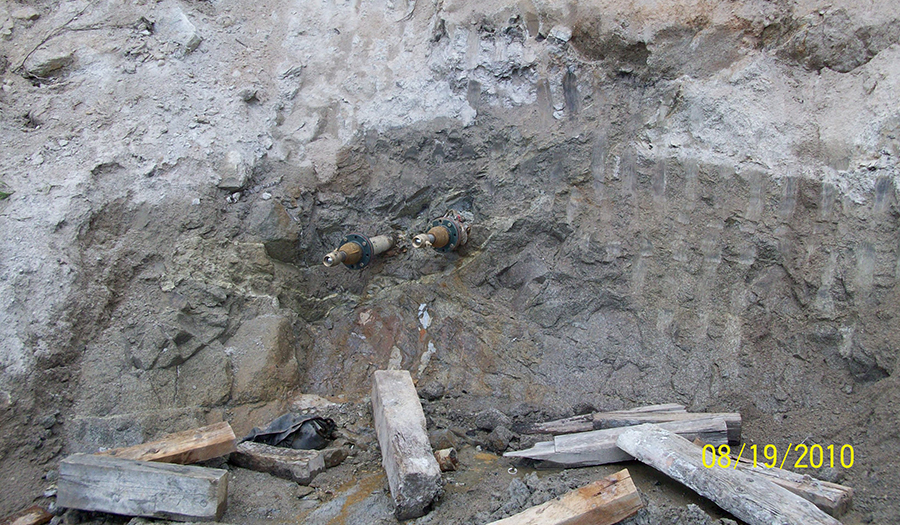
- Waste rock, tailings, and sediment are sources of arsenic and metals to Uncle Sam Gulch Creek
- Surface water and groundwater infiltrate into mine workings and create about 25-40 gpm of acid mine drainage











